What to Expect During a Stress Test?
Whether you’ve recently experienced symptoms like chest discomfort or shortness of breath, or your physician is just proactively monitoring your heart health, your doctor may recommend stress testing as an early diagnostic tool. While stress testing is just one of the many advanced services available to help detect and prevent cardiovascular disease early, it’s also one that few people know much about.
So, what should you expect during a stress test? It’s a common enough question, especially for anyone visiting a cardiologist for the very first time. Knowing what to expect gives you the confidence to walk into your appointment informed and ready.
What to Expect During a Stress Test?
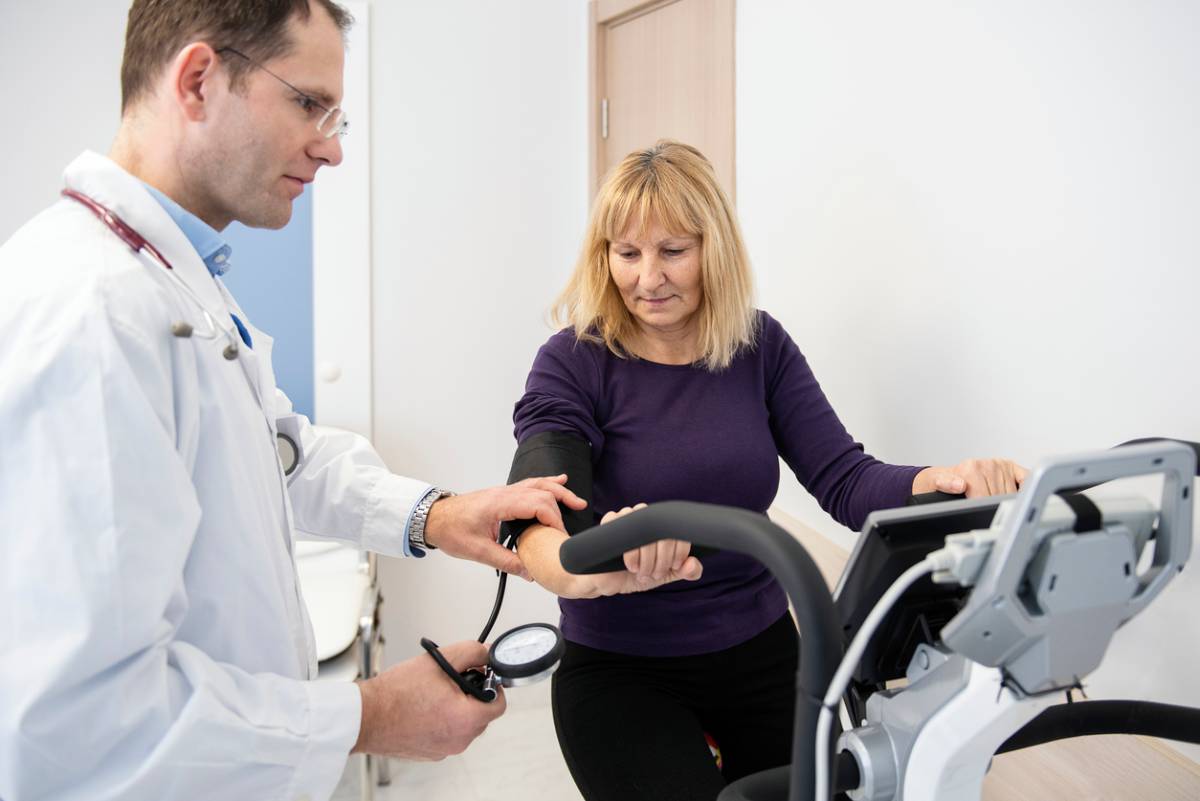
A stress test, otherwise known as an exercise stress test or sometimes even a treadmill test, is a way for your cardiologist to see how well your heart functions under physical exertion. While resting heart data provides some insight into your heart health, it doesn’t tell nearly the whole story. By having you exercise, your cardiologist can monitor how your heart responds when it’s working harder. Don’t worry; you won’t be asked to lift your weight in barbells or keep a sprinter’s pace for a mile. Doctors typically ask patients to walk or jog on a treadmill for a few minutes and nothing more.
During the test, you’ll be connected to an electrocardiogram (EKG) machine that continuously records your heart’s electrical activity. A blood pressure cuff will also be used to monitor changes throughout the test. They may also observe your breathing.
The test will start you off at a slow walking pace and gradually increase in difficulty. If this sounds stressful, keep in mind that the process is supervised every step of the way by trained medical professionals, so you will not reach the point of overexertion. The goal isn’t to push you to your limit but to evaluate your heart’s performance under stress.
Understanding Different Types of Stress Testing
At Apex Cardiology, stress testing is customized based on your unique health profile. While the treadmill test is common, other forms may be used, such as pharmacologic stress testing, which is often a better choice for patients who are unable to exercise due to physical limitations.
Some stress tests are paired with imaging, like nuclear scans or echocardiograms, to provide visual insight into how blood flows through the heart or how well it pumps during increased activity. Your cardiologist will select the most appropriate type to give the clearest picture of your cardiovascular function.
How Long Does a Stress Test Take, and What Should I Expect Physically?
The entire visit for your stress test usually takes about 45 minutes to an hour. The actual exercise portion generally lasts between 10 and 15 minutes. This depends on your fitness level and how long your heart can safely maintain an increased workload.
You’ll be asked to wear comfortable clothing and walking shoes as if you’re heading out for a light workout. Before the exercise begins, a technician will place small, sticky electrode patches on your chest to monitor heart rhythms. A baseline reading will be taken before you begin moving.
As the treadmill speeds up and inclines, you’ll be asked to report any symptoms, such as dizziness, shortness of breath, or chest pain. These are all key clues your cardiologist uses to interpret results.
Can I Eat or Take Medications Before My Stress Test?
Your cardiologist will provide detailed instructions tailored to your specific medical background. Still, in general, you may be asked not to eat or drink anything except water for a few hours before the test. Certain medications may also be paused before testing, especially if they affect heart rate or blood pressure.
If you have diabetes or are taking beta-blockers, make sure to inform your care team ahead of time. The goal is to make sure that the test results accurately reflect your natural heart response. Planning ahead and following pre-test instructions closely ensures the data your cardiologist receives is as precise and meaningful as possible.
What Happens After the Stress Test?
Once the treadmill portion is complete, your heart will continue to be monitored during the recovery phase. This helps your care team see how quickly your heart rate returns to normal, an important indicator of cardiac health. You’ll be able to cool down and rest while the equipment gathers final readings.
Results are not always immediate, as your cardiologist may need to review the data in detail, sometimes alongside imaging studies if a nuclear or echocardiographic stress test is ordered. They’ll follow up with insights and next steps, which might include further testing, lifestyle recommendations, or a change in your treatment plan if needed.
Ready to Schedule Your Stress Test?
If your physician or cardiologist has recommended a stress test or if you’re experiencing symptoms and want peace of mind, the expert team at Apex Cardiology is here to guide you through every step. Schedule your consultation today and take the next step toward proactive heart health.